How to calculate the power of a number in python
To calculate the power elevation of a number in python, it use the pow() function.
pow(a,b)
- The first argument (a) is the basis of the number to be raised to power.
- The second argument (b) is the exponent of power.
The function returns the power of the number raised to b.
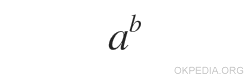
Note. If the exponent (b) is between 0 and 1, the function calculates the root of the number. For example, if the exponent is 1/2 the pow (a, 1/2) function calculates the square root of the base by a well-known rule of mathematical equivalence between elevation to power and root.
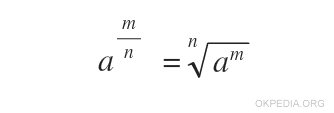
Practical examples
Example 1 (squared elevation)
This instruction calculates the number 4 raised to the square.
pow(4,2)
16
The result is equivalent to 4 * 4 = 16
Example 2 (cube elevation)
This instruction calculates the power of the number 2 raised to the cube.
pow(2,3)
8
The result is equivalent to 2*2*2=8
Example 3 ( nth root )
If the exponent is a fractional number 1/n between 0 and 1, the pow function calculates the nth root of the number (radicando) with index n.
This instruction calculates the square root of the number 9
pow(9,1/2)
3
The result is the square root (1/2) of the number 9.
To make the cubic root
pow(27,1/3)
3
The result is the cubic root (1/3) of the number 27.
